How Dropshipping and Print on Demand Work: A Simple Guide for Beginners

Dropshipping and Print on Demand (POD) have become popular because they let you sell products online without holding inventory – Dropshipping vs print on demand.
You don’t manufacture products.
You don’t store them.
You don’t ship them yourself.
Instead, you focus on:
- Choosing products
- Marketing and branding
- Customer experience
Let’s break down how each model works, step by step.
What Is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is an ecommerce model where you sell products that are shipped directly from a supplier to the customer.
You act as the middle layer between the buyer and the supplier.
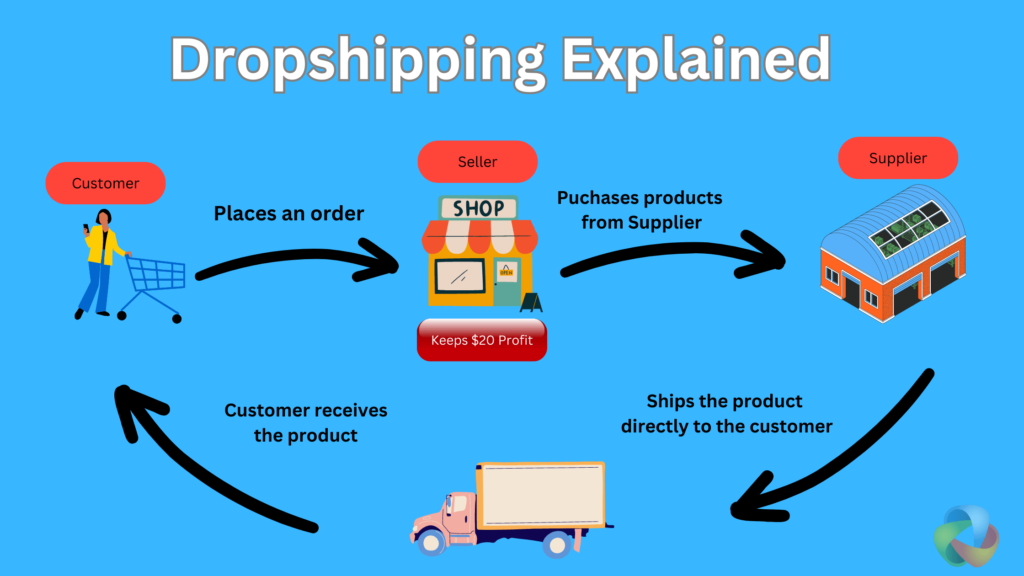
How Dropshipping Works (Step by Step)
Step 1: You Set Up an Online Store
You create an online store using platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce.
You list products from a supplier at a marked-up price.
Step 2: A Customer Places an Order
A customer buys a product from your store and pays you, not the supplier.
This includes:
- Product price
- Your profit margin
Step 3: You Forward the Order to the Supplier
You place the same order with your supplier (often via platforms like AliExpress), paying them the wholesale price.
Step 4: Supplier Ships the Product
The supplier ships the product directly to the customer, usually without your branding.
You never touch the product.
Step 5: You Handle Customer Support
You’re responsible for:
- Customer queries
- Refunds and disputes
- Delivery issues
How You Make Money in Dropshipping
Your profit =
Selling price – Supplier cost – Ads – Platform fees
Margins are usually:
- Low to medium
- Volume-driven
Pros and Cons of Dropshipping
✅ Pros
- Very low startup cost
- No inventory risk
- Easy to start
- Scalable
❌ Cons
- High competition
- Low profit margins
- Shipping delays
- Limited quality control
What Is Print on Demand (POD)?
Print on Demand is a variation of dropshipping — but with customised products.
You sell products like:
- T-shirts
- Hoodies
- Mugs
- Phone cases
- Posters
These items are printed only after a customer places an order.
How Print on Demand Works (Step by Step)
Step 1: You Create Designs
You design graphics, text, or artwork for products.
These designs are uploaded to POD platforms like Printify or Printful.

Step 2: You Connect POD Platform to Your Store
Your store (Shopify, Etsy, etc.) is integrated with the POD service.
Products sync automatically.
Step 3: Customer Places an Order
A customer orders a custom product from your store.
Step 4: Product Is Printed and Shipped
The POD provider:
- Prints the design
- Packages the product
- Ships it directly to the customer
Step 5: You Handle Branding and Marketing
Unlike dropshipping, POD allows:
- Custom branding
- Niche targeting
- Brand loyalty
How You Make Money in Print on Demand
Your profit =
Selling price – Printing cost – Platform fees – Marketing
Margins are generally:
- Higher than dropshipping
- Brand-driven
Dropshipping vs Print on Demand: Key Differences
| Feature | Dropshipping | Print on Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | No | No |
| Customisation | No | Yes |
| Branding | Limited | Strong |
| Competition | Very high | Medium |
| Profit potential | Lower | Higher |
| Long-term brand | Difficult | Easier |
Which Model Is Better for Beginners?
Choose Dropshipping If:
- You want to test products quickly
- You’re focused on paid ads
- You want speed over branding
Choose Print on Demand If:
- You want to build a brand
- You enjoy design or niche marketing
- You want long-term value
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Choosing generic products
- Ignoring shipping times
- Poor customer support
- Over-reliance on ads
- No brand differentiation
Let’s start the Journey:
Dropshipping and Print on Demand are business models, not shortcuts – Dropshipping vs print on demand.
They work best when you:
- Understand your niche
- Focus on customer trust
- Build systems, not hype
If done right, both can become scalable online businesses — but POD generally offers better long-term sustainability.
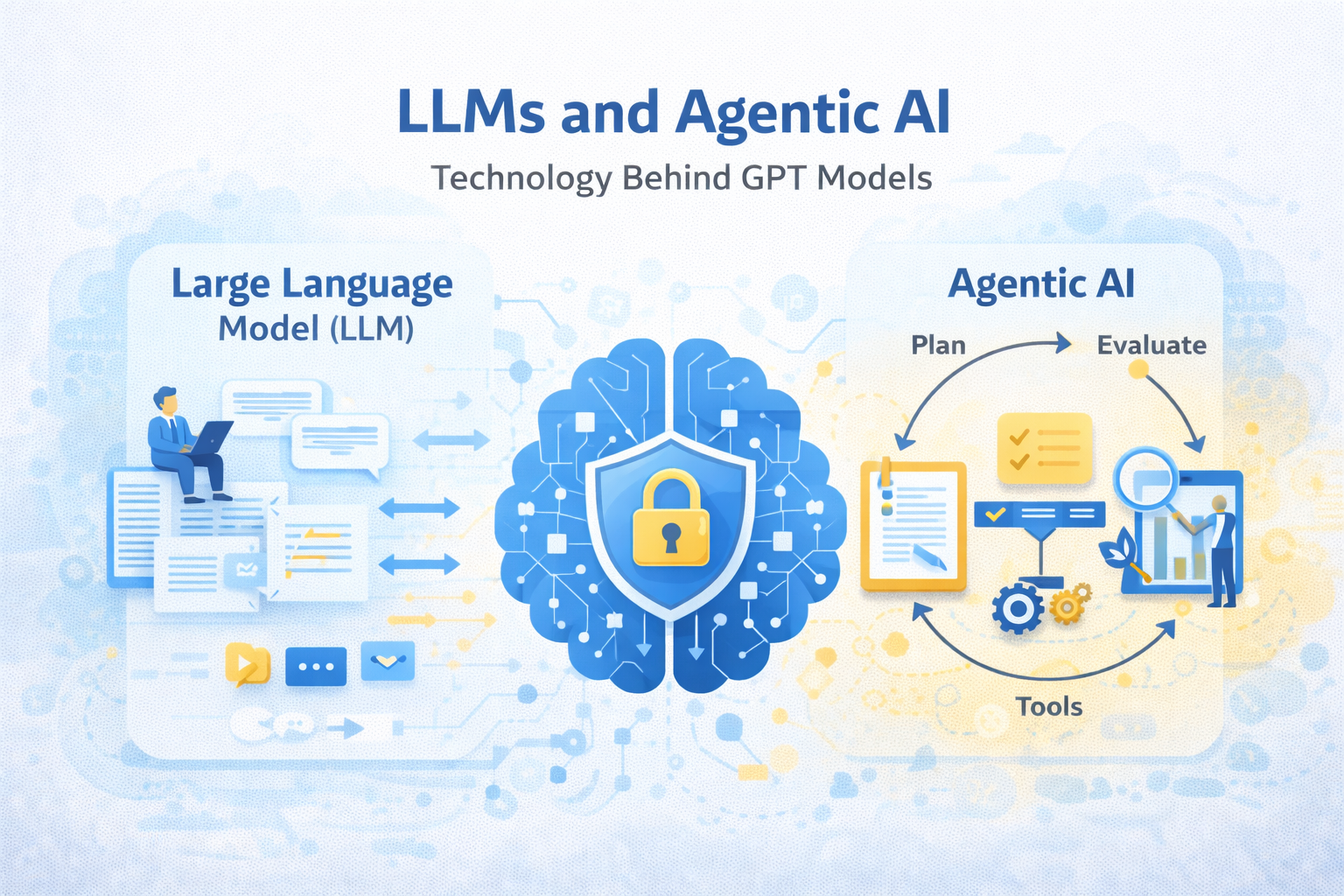
Read the article on : – LLMs and Agentic AI Explained: How GPT Models Really Work